What Is Found In Plant Animal And Bacterial Cells
Main Difference – Bacterial Cell vs Animal Cell
Bacterial and animate being prison cell are two kinds of living cells constitute in nature. Bacterial cells belong to the kingdom: Monera and animal cells belong to the kingdom: animalia. Since bacterial cells are prokaryotic cells, they do not membrane-leap organelles. All the cellular contents are openly accessible within the cytoplasm in prokaryotes. Animal cells consist of membrane-leap organelles such every bit nucleus and mitochondria. This is the principal difference between bacterial cell and animal jail cell.
This article looks at,
1. What is a Bacterial Jail cell
– Cellular Construction, Classification, Metabolism
two. What is an Animal Cell
– Characteristics, Cellular Construction
three. What is the divergence between Bacterial Cell and Animal Cell

What is a Bacterial Prison cell
Bacterial cells are prokaryotes, which can be considered equally simple, unicellular microorganisms. They are lacking membrane-bound organelles like nucleus and mitochondria. Bacteria are found in habitats such equally soil, water, acidic hot springs, deep portions of World'southward crust and radioactive waste. They live in either symbiotic or parasitic relationships with plants and animals. By attaching to surfaces, bacteria form dumbo aggregations like a mat. These bacterial mats are called biofilms.
Cellular Structure of Bacterial Cell
Bacterial cells are 0.2 to 2 µm in size. The cell is surrounded past a jail cell membrane. The membrane-enclosed cytoplasm contains nutrients, proteins, DNA and other essential components of the cell. Modest 70S ribosomes are nowadays for the protein synthesis. Poly peptide localization is carried out past their primitive cytoskeleton. A single, circular chromosome is establish in the nucleoid. This uncomplicated arrangement of bacteria is referred to as 'bacterial hyperstructures'.
Murein forms a prison cell wall outside the bacterial prison cell membrane. The prison cell wall provides protection to the cell, maintains the shape and prevents the cell from dehydration. The thicker jail cell wall is classified every bit gram-positive and the thinner cell wall is classified as gram-negative in the gram staining of bacteria. Flagella are used for the mobility of the cell. The entire cell is covered past glycocalyx which forms the capsule.
Some genera of gram-positive bacteria form a resistant, fallow structures called endospores. Endospores contain some parts of the cytoplasm, Dna and ribosomes covered by a cortex. They are resistant to radiation, detergents, disinfectants, heat, freezing, pressure and desiccation. Bacterial cells reproduce asexually by binary fission and sexually by conjugation. A generalized structure of a gram-positive bacterial cell is shown in figure 1.
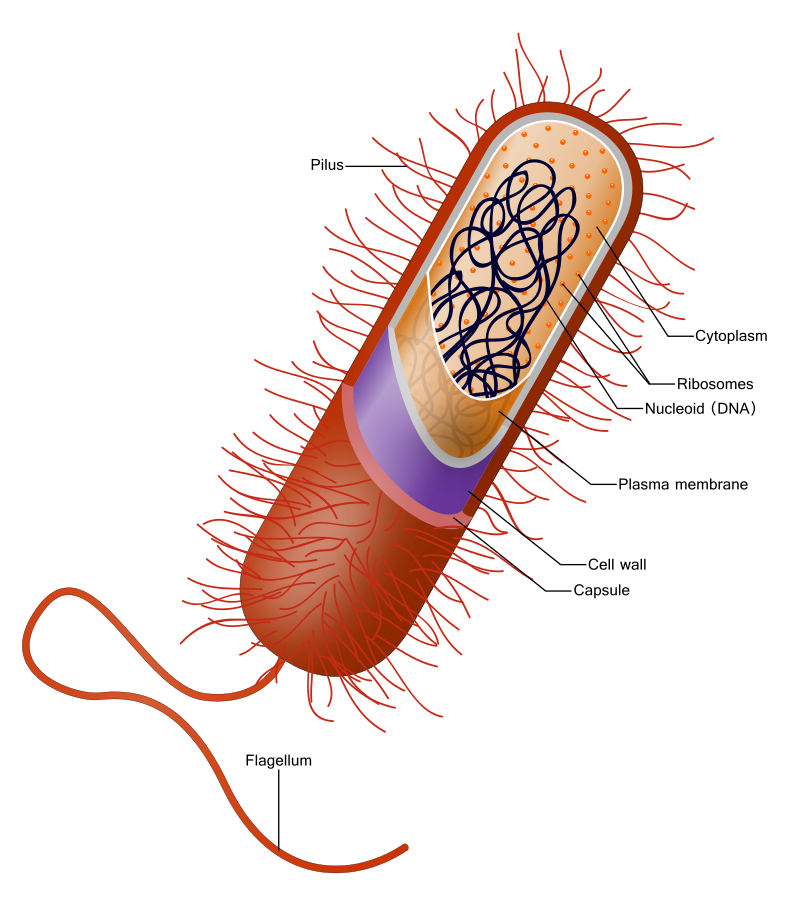
Effigy 1: Generalized gram-positive bacterial cell
Classification of Bacterial Cell
Leaner tin be categorized depending on their morphology:
- Cocci are the spherical-shaped bacteria.
- Bacillus are the rod-shaped bacteria.
- Vibrio are the comma-shaped bacteria
- Spirilla are the screw-shaped leaner
- Spirochaetes are tightly coiled bacteria
Some leaner alive as single cells. Just, some of them live in pairs called diploids. Streptococcus are the bacterial bondage. Staphylococcus form 'agglomeration of grapes' like clusters. Filaments are the elongated bacteria like Actinobacteria. Some are branched filaments such as Nocardia.
Metabolism
Depending on the carbon source, leaner tin be divided into 2 groups: heterotrophs and autotrophs. The carbon source is organic compounds in heterotrophps whereas the carbon source is carbon dioxide in autotrophs. Depending on the energy source, bacteria can be divided into 3 groups: phototrophs, lithotrophs or organotrophs. In the phototrophs, the free energy source is sunlight. Organic compounds are used as the energy source in organotrophs. In lithotrophs, the energy source is inorganic compounds.
What is an Animate being Prison cell
Animal cell can course either unicellular or multicellular eukaryotic organisms, containing membrane-enclosed organelles such as nucleus, mitochondria and Golgi appliance. Multicellular eukaryotes contain specialized tissues made past different types of cells. Approximately 210 distinct animal cell types can be establish in the adult human body. They have various functions like the production of enzymes, hormones and energy. Creature cells are heterotrophs.
Cellular Structure of Animal Cell
Animal cells are larger in size compared to bacterial cells and are nigh ten to 100 µm in size. They are irregular in shape due to the lack of a prison cell wall. The outer purlieus of an animal cell is the plasma membrane, which is considered as semi-permeable. Semi-permeable membranes simply let selected molecules to movement across it. Plasma membrane is composed of phospholipids containing polor heads and non-polor tails. It is described by the lipid bi-layer model.
Cytoskeleton of the animal cell is composed of microfilaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments. Cytoskeleton plays a vital role in cellular organization and its shape. Animmal cells are composed of a variety of membrane-spring organelles. The nucleus is enclosed by two membranes called nuclear membrane or nuclear envelop. Nuclear membrane forms the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which is involved in protein maturation and transportation. Ribosomes are large, 80S in size and are jump to the ER. Ribosome-leap ER is referred to as rough ER. Vesicles are present for the transformation of diverse molecules within the cell such equally golgi bodies, lysosomes and peroxizomes. Lysosomes store digestive enzymes. Mitochondria is as well surrounded by 2 phospholipid bilayers. They covert sugar into ATPs in order to employ it as energy. Animate being cells incorporate structures like cilia, centrioles, flagella and lysosomes. A generalized creature prison cell is shown in figure 2.

Effigy 2: Generalized animal cell
Usually, creature cells are equanimous of more than than i chromosomes in the nucleus. These chromosomes are linear and often exist in multiple copies called homologous. Animal cells reproduce asexually past mitosis and sexually past meiosis, followed by the fusion of gametes.
Difference Between Bacterial Cell and Animal Cell
Blazon
Bacterial cell: Bacterial cell is a prokaryotic cell.
Animal prison cell: Beast cell is a eukaryotic cell.
Size
Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells are 0.2 to two µm in size.
Animal Cell: Animal cells are larger in size compared to bacterial cells and 10 to 100 µm in size.
Cell wall
Bacterial Cell: The bacterial cell wall is made up of murein.
Creature Prison cell: Brute cells do not take a cell wall. The plasma membrane is the outer purlieus.
Shape
Bacterial Jail cell: Bacterial cells consist of several shapes like coccui, bacillus, vibrio, spirilla.
Animal Prison cell: Animal cells are irregular in shape due to the lack of a cell wall.
Jail cell Nucleus
Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells exercise non possess a nucleus.
Animal Cell: Animal cells are composed of a membrane-spring nucleus.
Plasmids
Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cytoplasm has plasmids.
Animate being Cell: Animal cells practice not have plasmids.
Mitochondria
Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells do not contain mitochondria.
Animal Jail cell: Animal cells contain mitochondria in the cytoplasm.
Ribosomes
Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells contain 70S, small ribosomes.
Creature Cell: Animal cells contains 80S, larger ribosomes.
Centrioles
Bacterial Prison cell: Bacterial cells do not contain centrioles.
Animal Cell: Animal cells contain centrioles.
Lysosomes
Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells do not contain lysosomes.
Animal Jail cell: Animate being cells contain lysosomes.
Metabolism
Bacterial Prison cell: Bacterial cells tin can be either heterotrophs or autotrophs.
Animal Cell: Fauna cells are heterotrophs.
Reproduction
Bacterial Prison cell: Bacterial cells reproduce asexually by binary fission and sexually by conjugation.
Animal Cell: Animate being cells reproduce asexually by mitosis and sexually past meiosis, followed past the fusion of gametes.
Decision
Bacterial cells and brute cells can exist considered equally independent units, conveying out cellular metabolism and reproduction without the aid of other cells. Bacterial cells incorporate a primitive origin compared to animal cells. Bacterial ribosomes are smaller than the animals' ribosomes. Besides, animal cells comprise membrane-bound organelles like nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and ER. On the contrary, bacterial cells lack membrane-leap organelles. Bacterial chromosomes are localized to an area in the cytoplasm chosen every bit nucleoid. The main difference between bacterial jail cell and animal cell is their cellular organization.
Reference:
i. "Bacterial cell structure". Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 2017. Accessed 01 March 2017
ii."What's in a prison cell?". BBC, 2014. Accessed 01 March 2017
3."Eukaryote". Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 2017. Accessed 01 March 2017
Image Courtesy:
one. "Prokaryote cell"Past Ali Zifan – Own piece of work; used information from Biology 10e Textbook (affiliate four, Pg: 63) by: Peter Raven, Kenneth Stonemason, Jonathan Losos, Susan Vocalist · McGraw-Hill Education. (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ii."Animal cell construction en" By LadyofHats (Mariana Ruiz) – Own work . Image renamed from Image: Animal cell structure.svg (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia

Source: https://pediaa.com/difference-between-bacterial-cell-and-animal-cell/
Posted by: hollandwoorkepark.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is Found In Plant Animal And Bacterial Cells"
Post a Comment